What is a Long Strangle?
A strangle option strategy is a basic volatility strategy which comes with low risk but will require dramatic price moves to pay out profitably. The strangle calls for buying out of the money puts and out of the money calls with different strike prices but the same expiration date. While the risk characteristics are slightly different, the strangle is very similar to the straddle in that it has two breakeven points and many of the other basic principles are similar.
Strangle Risk Characteristics
Let's review the basic strangle risk characteristics graph so that we can better understand the risks and rewards associated to this strategy. As opposed to most of the other option strategies we have discussed, you can see that the strangle has two breakeven points. While the strangle has lower risk associated to it, the probability of profit is also less than that of the straddle as the breakeven points are further away. The general rule of thumb when purchasing a strangle is to buy the put and the call with strike prices equal in distance from the current price. For example, if the security was trading at $25, you would purchase the $20 put and the $30 call.
Options strategy - Strangle
_________________________________________________________

Long Straddle
Since you are buying both of the options, your risk is limited to the the amount you pay for both combined:
Risk = Call Premium + Put Premium
Since this is a net credit transaction with two long options, the breakeven in either direction is just the strike price +/- Options premiums.
Breakeven on the Upside (*b2 in diagram) = Strike Price + Call Premium + Put Premium
Breakeven on the Downside (*b1 in diagram) = Strike Price - Call Premium - Put Premium
The profit potential of this strategy is unlimited after breakeven.
To be precise, the total profit/loss at expiration can be calculated with the following two formulas:
Profit/Loss at Expiration = Absolute Value(Security Closing Price - Strike Price) - Risk
Straddle Example
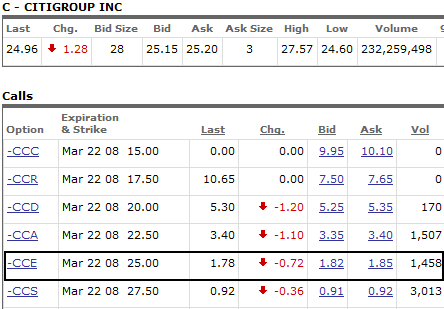
Let's use Citigroup (C) to create a straddle example.
Call Option Chain:
Put Option Chain:

The stock is trading at $24.96 as of today's closing price. Therefore, we will buy the two month, at the money, option at $25. It is currently Jan of 2008 and I selected options with 2 months till expiration. I did this for example purposes since the three month chain is not available as of yet. Typically, you want to allow yourself at least 3 months of time for this trade to work out. Remember, once the option has less than 30 days, the time premium (theta) starts to decay at a more rapid pace. You want to allow yourself enough time in case the trade does not work out immediately. Personally, I do not hold straddle's that are 30 days left till expiration. At that point, the security has not made the move I was looking for and I cut my losses while the time premium is still reasonably high. Secondly, if you are trading the straddle for an earnings release and the stock does not react with a strong move, you should consider selling the straddle after a couple days pass with no movement.
To set up the Citi straddle, we will pay $1.85 for the 25 calls and $2.04 for the 25 put. Notice how the price of the put is greater even when the stock is trading right near the strike. This occurs due to the market premium that is being given to protection on the downside. The market is currently getting hammered and there is a large demand for puts. Supply and demand forces have an influence on option prices.
In any case, we are paying $3.89 for both options and this becomes the risk of the straddle. The expectation is that the stock will break above $28.89 or break below $21.11 before options expiration. If either scenario occurs, this straddle will be in a profit position. Ideally, you want to look for at least a 1:1 reward to risk ratio. Therefore, we want to see Citigroup above 32.78 or below $17.22 to make it worth your time and risk.
In conclusion, the straddle is a great idea if you expect the security to move substantially, but do not know which way. It can come with a relatively high cost but your risk is limited to what you put into it, as opposed to a short straddle. Remember that you are playing the expectation for volatility to increase and if it does not when you expect it to, think about selling the straddle to avoid bleeding time value.
Related Topics
Options strategies:
----------- EDUCATION ---------
-------TRADING METHODS ------
--------- FOR TRADERS ----------
-------------- OTHER ------------
---------------------------------------------

_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________